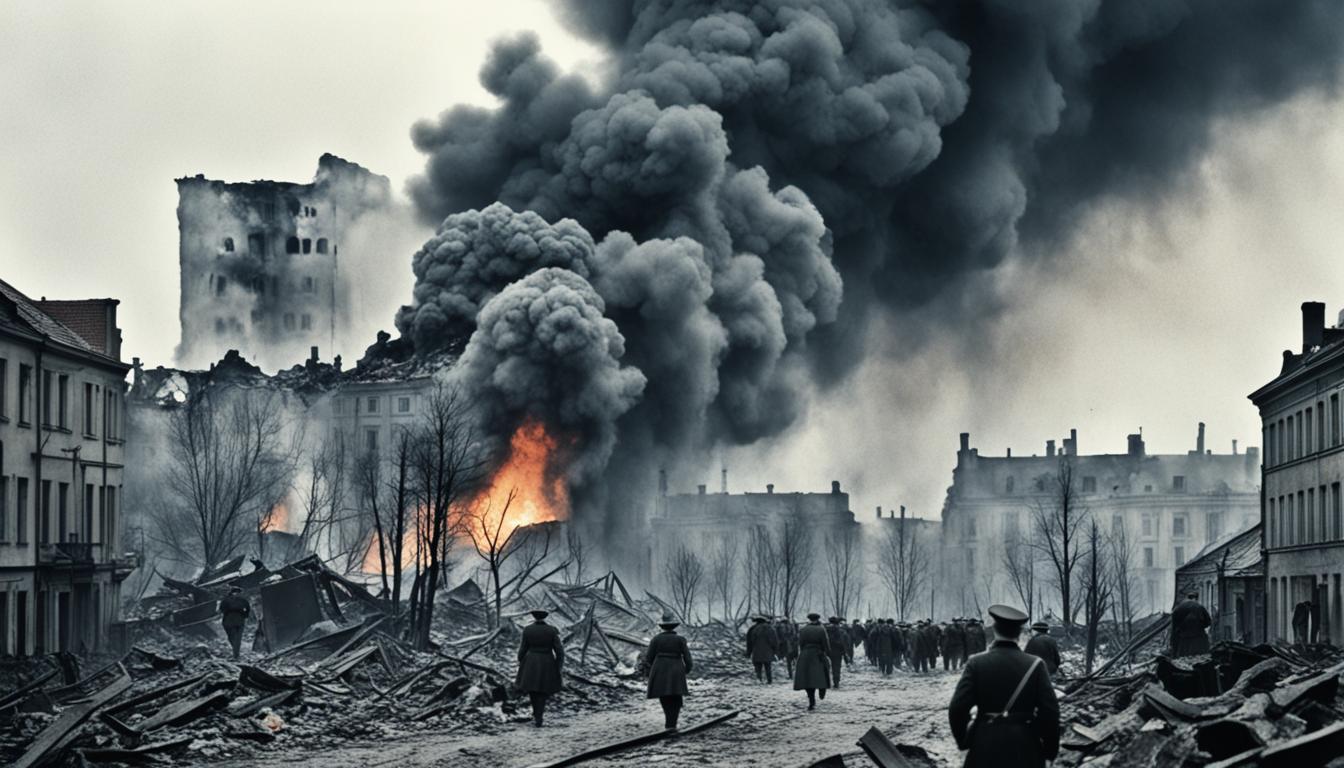
The invasion of Poland in 1939 by Nazi Germany was a pivotal event in European history. It marked the start of a devastating global conflict. On September 1st, 1939, German troops entered Polish land, ending efforts to keep peace after World War I.
This attack quickly led to a full-scale military conflict. It signalled the beginning of the Second World War. This war changed international relations and warfare for many years to come.
Key Takeaways
- The invasion by Nazi Germany directly led to the outbreak of the Second World War.
- Preceding the invasion was a series of failed international diplomatic efforts.
- The 1939 Poland invasion was a stark example of Nazi Germany’s expansionist policies.
- The European history of the early 20th century was shaped profoundly by this military conflict.
- Global war necessitates studying the events leading up to the invasion to understand the complexities of the period.
- The invasion’s historical significance lies in its role as the catalyst for wider global conflict.
The Prelude to the Invasion of Poland
Before Poland was invaded in 1939, Europe was very unstable. The Versailles Treaty after World War I made this worse, especially for Germany. This affected how Germany and Poland got along. Poland tried hard to keep its country safe and sovereign. It made many pacts with other countries. The most important of these was with Britain. This showed how complex and tricky global diplomacy was back then.

Interwar Relations and Treaties
The Versailles Treaty had a big impact between the World Wars. It changed the map and politics of Europe. It also made people very unhappy with the situation. This unhappiness led to Germany using military force later. Poland had to deal with these tough situations. Its relationship with Germany was careful but tense. This showed how peace in Europe was very fragile.
Military Mobilisation and Strategy
As Europe moved closer to war, Germany and Poland prepared their forces. Germany was planning a new way to fight. Poland was getting ready to defend itself. Both sides tried to understand the other’s plans. Sometimes they got it wrong. Germany’s plans were very detailed. Poland was not as strong, but it was determined to defend itself.
International Reactions and Failed Diplomacy
The League of Nations was supposed to help keep peace. But it didn’t work well because countries were focused on their own goals. The world didn’t react strongly enough to the signs of coming war. International laws were ignored. Talks between countries did not stop the war from happening. This period showed the weakness of trying to keep peace in the world, leading to a huge conflict.
Invasion of Poland: The Opening Act of World War II
In 1939, German forces entered Poland, starting the Second World War with a bang. They used blitzkrieg tactics, showcasing a new, fast way of fighting. This style of warfare outmatched traditional defence strategies.
The Blitzkrieg Strategy and its Execution
Blitzkrieg, or lightning war, revolutionised how wars were fought. Its first test was in Poland. Speedy and strong, the German army, with air support, broke through Poland’s defences quickly. They captured key areas, putting Warsaw under huge pressure.
Soviet Involvement: The Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact
Eastern Europe’s situation got more complicated with the Soviet-German peace pact. This deal led to the Soviets taking over part of Poland. It marked Poland’s division and had a big impact on the war’s political landscape.
The Resistance of the Polish Forces and Civilian Impact
The Polish military and civilians did their best to resist the German and Soviet forces. They defended Warsaw bravely but were overwhelmed. Civilians also suffered a lot, proving the invasion’s terrible human cost.
This invasion showed how brutal and fast modern wars could be. It marked the beginning of a worldwide fight, reminding us of the dangers of aggression. It also taught us how important it is to be ready for threats.
Conclusion
The 1939 invasion of Poland started the Second World War. It was a brutal act that changed history. This event reshaped military conflict and affected European stability and global awareness. It reminds us of history’s lessons, which still influence today’s policies and strategies.
The invasion changed the world map and power balances. It led to the creation of the United Nations. This aimed to prevent future wars, shaping our views on international law and conflict resolution.
The invasion’s lessons stress ethics and moral duty in international affairs. Experts warn against repeating these mistakes and highlight the need for respect and legality. We must promote peace and cooperation for a fair global community.
FAQ
What triggered the outbreak of World War II?
Germany’s invasion of Poland on 1st September 1939 sparked World War II. This aggressive act broke many international agreements. It also challenged the peace set after World War I.
How did the Treaty of Versailles affect German-Polish relations before World War II?
The Treaty of Versailles put harsh conditions on Germany, causing resentment. This strain worsened German-Polish relations, leading to Poland’s invasion in 1939.
What were the strategic implications of the non-aggression pacts signed before the war?
Pacts like the one between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union had major impacts. They allowed Germany to invade Poland without Soviet interference. Also, they split Eastern Europe, affecting later military actions and territory control.
How did the international community react to the imminent invasion of Poland?
The global response to Poland’s invasion risk was mostly ineffective. Britain and France’s appeasement policies did not work. The League of Nations’ weakness also failed to stop Germany, leading to war.
What was the blitzkrieg strategy and how was it executed during the invasion of Poland?
Blitzkrieg was a fast attack using tanks, mechanised infantry, and planes. Germany used this during Poland’s invasion, leading to swift victories. This changed warfare in the 20th century.
What role did the Soviet Union play in the invasion of Poland?
The Soviet Union, by agreeing to the Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact with Germany, played a key role. This deal secretly split Poland and other countries into German and Soviet areas. It led to a joint attack on Poland.
How did Polish military and civilians respond to the invasion?
Despite being overwhelmed, Polish forces and people fiercely resisted. Defending cities like Warsaw showed their bravery. Their fight delayed the invaders but couldn’t stop Poland’s occupation.
What were the broader humanitarian impacts of the invasion on Polish society?
The invasion brought terrible suffering to Poland, including civilian deaths, displacement, and trauma. There were also war crimes against Poles, deeply scarring the nation.
How did the invasion of Poland influence post-war geopolitics?
Poland’s invasion affected war rules and post-war politics. It helped shape new borders, the United Nations creation, and future diplomacy efforts to avoid such conflicts.
What lessons were learned from the invasion of Poland in World War II?
The invasion highlighted the risks of appeasement and the need for a strong security system. It stressed following international law for peace and protecting civilians from war horrors.